In the fast-evolving world of lithium-ion batteries, the debate between winding and stacking methods often boils down to one question: which is better? As an OEM battery engineer with over a decade on the factory floor, I’ve seen both processes in action—from troubleshooting winding machines to optimizing stacking lines for global brands. The truth? It’s not about picking a winner. It’s about understanding the trade-offs in battery cell manufacturing processes that impact energy density, safety, yield, and real-world performance.
This guide breaks it down from an engineer’s perspective, drawing on firsthand experience rather than hype. Whether you’re researching wound vs stacked lithium batteries or diving into battery winding and stacking processes, you’ll get practical insights to inform your decisions. I’ve incorporated real data from industry sources, along with visuals like diagrams, photos, and graphs to make the concepts clearer.
What Are Winding and Stacking in Battery Cell Manufacturing?
At their core, winding and stacking are two primary ways to assemble the electrodes and separators inside a lithium-ion battery cell. These methods shape how the cell performs, from energy density in battery design to overall battery safety design.
What Is the Battery Winding Process?
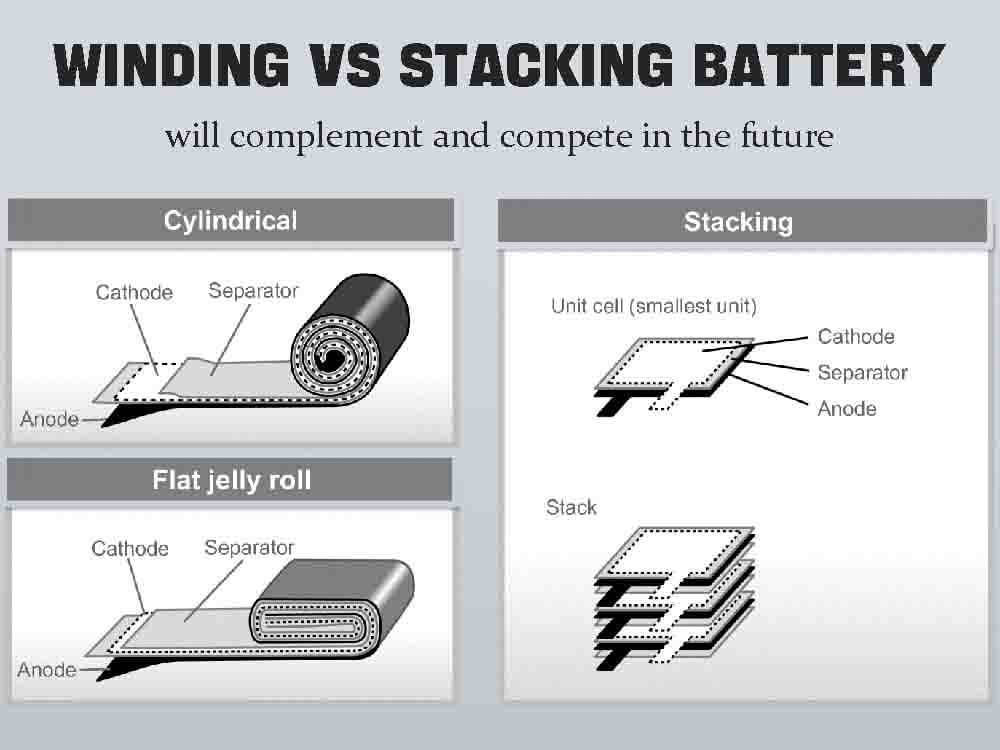
The winding process involves rolling the positive electrode, separator, and negative electrode into a tight spiral, much like a jelly roll. This technique is a staple in cylindrical cells, such as the popular 18650, 21700, and Tesla’s 4680 formats, and even some prismatic cells.
Key features:
- Continuous assembly: Materials are fed from rolls, wound at high speeds, and sealed.
- Efficiency focus: Ideal for high-volume production due to its speed and simplicity.
Structural diagram of battery cell winding machine | Download …
For comparison, another view of a wound cell assembly:
3 Different Shapes Lithium Battery Structures
And a real-world photo of a battery winding machine in operation:

The Heart of Lithium-Ion Battery Production: Winding Machines
What Is the Battery Stacking Process?
Stacking, on the other hand, cuts electrodes and separators into individual sheets and layers them flat, like stacking pancakes. This approach shines in pouch cells and elongated prismatic formats, where space efficiency is key.
Key features:
- Layered precision: Each layer is aligned and pressed, minimizing wasted space.
- Flexibility: Easier to customize for thin or irregular shapes.
Schematic illustration of the stack configuration in …
Another diagram showing stacked cell construction:

Understanding Cell and Battery Construction – Technical Articles
Both methods aim for the same goals—maximizing energy density while ensuring safety—but they take different paths based on the cell’s format and application.
The Evolution of Winding Technology: From Basic to High-Precision
Winding isn’t outdated; it’s continually refined to meet modern demands. In my years overseeing production lines, I’ve witnessed how innovations have turned common pitfalls into strengths. For instance, recent advancements have led to up to 25% higher energy density and 20% faster production speeds in optimized winding systems.
1. High-Speed Winding with Advanced Controls
Early winding suffered from defects like edge misalignment, wrinkles, or C-corner deformation (where the spiral bends sharply). Today’s machines incorporate:
- Tension control systems: Maintain even pressure to prevent creases.
- Real-time feedback: Sensors and cameras for instant adjustments.
- Online inspection: Catches issues mid-process, boosting yield rates.
Result? Line speeds of tens of meters per minute with minimal waste—essential for scaling battery cell manufacturing. Throughputs can reach 30 cell windings per minute for cylindrical cells.
2. Tab Innovations: Full-Tab and Tabless Designs
Tabs connect electrodes to the cell’s terminals, and winding has adapted here too:
- Full-tab and multi-tab setups: Reduce internal resistance for faster charging.
- Tabless concepts (like in 4680 cells): Eliminate tabs entirely for better heat dissipation and higher discharge rates.
Trade-offs: These require laser-precise slitting and folding, increasing complexity but enhancing performance in high-power applications.
3. Integrated Systems: Cut-to-Winding Hybrids
Modern setups combine cutting, winding, and initial forming in one machine:
- Benefits: Reduces handling damage, improves consistency, and shortens production cycles.
- Challenges: High costs and patent protections (e.g., LG’s proprietary hybrids) limit accessibility.
Why Stacking Is Gaining Ground: Uniformity and Performance Edges
Stacking has surged in popularity, especially for electric vehicles and consumer electronics, thanks to its inherent advantages in uniformity. Industry experts predict that by 2025, the adoption rate of stacking in high-end power batteries will exceed 60%.
The Fundamental Edge: No C-Corners
Unlike winding’s spirals, stacking avoids curved edges, leading to:
- Even stress distribution: Reduces internal hotspots and polarization.
- Superior cycle life: Stabler voltage and slower degradation, even at high depths of discharge.
From lab tests I’ve run, stacked cells often deliver more consistent performance over thousands of cycles. Stacked cells can have higher energy density, more stable structures, and better safety margins.
Modern Stacking Techniques: Z-Stacking and Integrated Lines
Traditional Z-stacking (folding layers in a zigzag) faced speed and alignment issues. Upgrades include:
- Cut-stack integration: Laser or die cutting paired with automated stacking and bonding.
- Reduced errors: Minimizes manual intervention, cutting micro-damage and boosting yield.
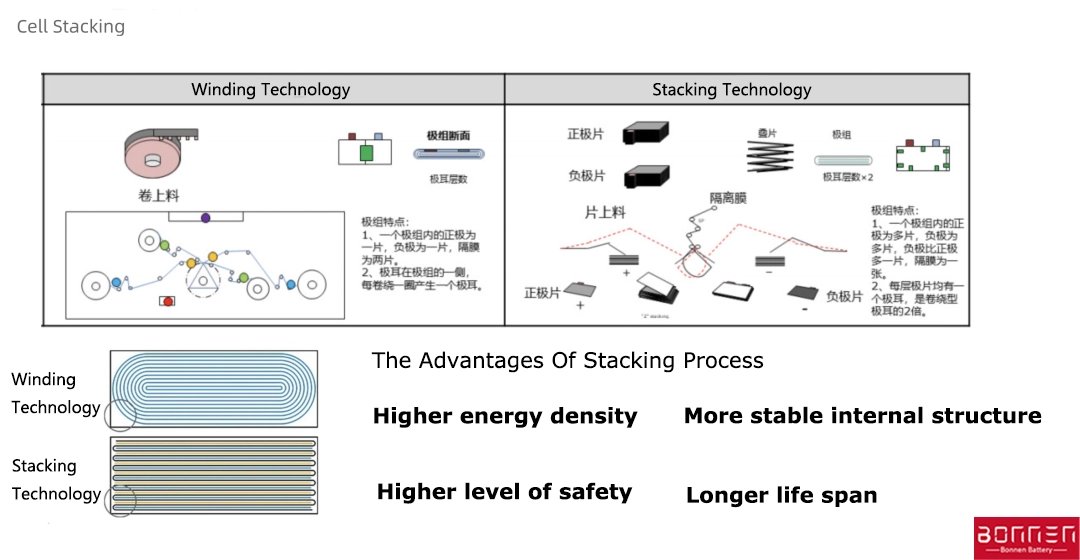
Speeds are now rivaling winding, making it viable for mass production, with stacking rates up to 0.15 seconds per sheet. A visual of stacking vs winding technology:
What is Cell Stacking Technology? | Grepow High Power Lithium Battery
Advanced Thermal Composite Stacking
This cutting-edge method applies heat and pressure during stacking:
- Uniform interfaces: Improves electrolyte flow and pore distribution.
- Denser packs: Enhances energy density in battery design.
Downsides? Steep equipment costs and tight process controls—but the safety gains are worth it for premium applications.
Winding vs Stacking: Key Engineering Trade-Offs
Here’s a head-to-head comparison based on real-world metrics. Remember, these are generalizations; actual results vary by design and materials. Data shows stacking can increase energy density by about 5% compared to winding. Stacking also offers higher safety and longer cycle life, though with potentially lower initial yields.
| Dimension | Winding | Stacking |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Good (spiral packing efficiency) | Excellent (flatter, space-optimized layers; up to 5% higher) |
| Internal Resistance | Moderate (tabs can add resistance) | Lower (direct layering reduces paths) |
| Thermal Behavior | Good, especially in cylindrical formats for even heat spread | More uniform, easier to manage in flat designs |
| Safety Margin | Mature with proven track records | Generally higher due to reduced stress points |
| Production Speed | Very high (continuous process; 30 cells/min) | Improving rapidly with automation (0.15 s/sheet) |
| Equipment Cost | Lower (simpler machinery) | Higher (precision stacking tech) |
| Best Formats | Cylindrical (e.g., 18650, 4680), some prismatic | Pouch, long/thin prismatic |
A graphical comparison of energy density between winding and stacking:
Winding Vs Stacking, Which Works Best For Lithium-Ion Batteries …
Another chart highlighting differences:
Winding vs stacking battery-pros and cons – TYCORUN ENERGY
For safety, here’s a chart on battery safety aspects in winding vs stacking:

This is why NCM is the preferable Cathode material for Li-ion …
And a detailed safety analysis graph:
Safety Analysis of Lithium-Ion Cylindrical Batteries Using Design …
This table and visuals highlight why neither method dominates—they complement each other based on the battery’s goals.
Real-World Applications: Why Both Methods Coexist
In projects I’ve led, the choice isn’t ideological; it’s practical.
- Cylindrical Cells (e.g., 18650/21700/4680): Winding wins for its speed and maturity, powering everything from laptops to EVs.
- Pouch and Prismatic Cells: Stacking excels in energy density and safety, ideal for slim devices and high-capacity packs.
- Hybrid Innovations: Large formats like 4680 push winding limits with tabless designs, while stacking adapts for ultra-thin applications.
It’s a division of labor: Winding for efficiency in established markets, stacking for cutting-edge performance. Stacking enables consistent internal alignment for higher capacities and improved safety over traditional winding.
A Personal Engineering Story: Trade-Offs in Action
On one consumer electronics project, we evaluated both:
- Winding advantages: Quick ramp-up, lower upfront costs, and reliable yields for high-volume runs.
- Stacking benefits: Superior long-term stability and thermal control under heavy loads.
We chose based on margins—ensuring safety, certification, and cost targets. That’s the real engineering mindset: balance over buzzwords.
Key Takeaways on Winding vs Stacking Battery Cells
- Strategies, Not Labels: Both are valid manufacturing philosophies tailored to specific needs.
- Core Strengths: Stacking boosts energy density and uniformity; winding prioritizes speed and cost-effectiveness.
- Future Outlook: Expect hybrids and optimizations as batteries evolve for diverse use cases, with stacking gaining traction in high-end markets.
Grasping these nuances goes beyond spec sheets—it equips you for smarter design choices.
About the Author
As a battery and power bank engineer at Reachinno, I’ve dedicated over 10 years to lithium-ion tech. From debugging production lines to certifying products for global brands, my insights come from hands-on work with wound and stacked designs across cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch formats. Connect with me on LinkedIn for more on battery safety, manufacturing, and innovation.

