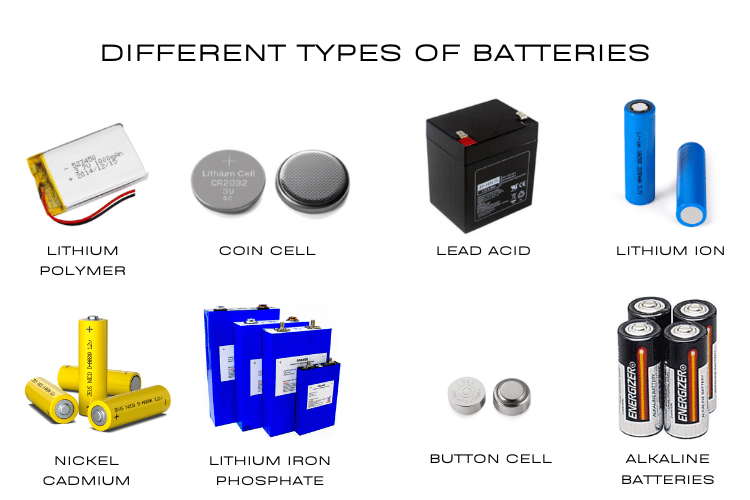
Types of Batteries: Complete Guide to 50+ Battery Types (2025)
The rapid growth of mobile devices, e-mobility, and energy storage has made power bank performance and safety more critical than ever. At the core of every high-quality power bank is its battery chemistry. For OEM/ODM brands sourcing power banks for EU and US markets, understanding the differences between Li-ion, Li-Polymer, LFP, semi-solid, and solid-state batteries is essential to meet safety, efficiency, and consumer expectations.
This guide explains the materials, chemistry, and performance characteristics of each battery type, along with their advantages and trade-offs in real-world applications. Drawing from expert sources on battery materials, overheating risks, and emerging technologies, we’ll help you choose the best for your needs.
1. Lithium-Ion Batteries (Li-ion)
Overview
Lithium-ion batteries dominate the power bank market due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and established safety standards. They are usually cylindrical (e.g., 18650: 18mm diameter, 65mm length for balanced capacity; 21700: 21mm diameter, 70mm length for higher efficiency) or prismatic cells. Composition includes graphite anodes, lithium salt electrolytes in organic solvents, and varying cathodes.
Common Chemistries
- LCO (Lithium Cobalt Oxide): High energy density, popular in compact high-capacity devices; slightly lower safety under thermal stress.
- NCM (Nickel-Cobalt-Manganese): Balanced energy, power, and safety; widely used in consumer power banks with models like 18650/21700.
- NCA (Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum): Extremely high energy density; mostly in high-end devices, offering up to 260 Wh/kg.
Advantages
- High voltage (3.6-3.7V per cell), ideal for compact 500-1000mAh models in applications like remotes or medical devices.
- Mature supply chain with low self-discharge.
- Efficient fast charging protocols (PD, QC).
- Energy density: 150-260 Wh/kg; cycle life: 500-1,000.
Drawbacks
- Thermal sensitivity; requires robust BMS and protection circuits to prevent overheating from high currents or defects.
- Slightly heavier than Li-Po for the same capacity.

What battery chemistries are used in electric vehicles?
2. Lithium-Polymer Batteries (Li-Po)
Overview
Li-Po batteries use a gel-like polymer electrolyte instead of liquid, allowing slimmer, lightweight, and flexible shapes. Common models include 606090 (60x60x90mm for high capacity) and 1260100 (slim profiles).
Advantages
- Ultra-thin and flexible design (perfect for slim power banks).
- Lower risk of leakage compared to traditional Li-ion; enhanced safety.
- High discharge current capability.
- Energy density: 130-200 Wh/kg; cycle life: 500-800.
Drawbacks
- Slightly lower energy density than Li-ion.
- More sensitive to overcharging and overdischarging.
- Requires precise manufacturing for safety; higher cost.
Slim Size Wholesale Li-Polymer Battery Mobile Charger Portable 15W Wireless Magnetic PD 20W Fast Charging Power Bank 5000mAh
3. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
Overview
LFP batteries (also known as LiFePO4) offer enhanced safety and long cycle life at a slightly lower energy density. Common models: 26650 (high capacity/stable) and 32700 (durable).
Advantages
- High thermal stability; very safe for high-capacity power banks, resisting runaway up to 60°C higher than NCM.
- Over 2,000-3,000+ charge cycles.
- Lower internal resistance; reliable high-current output.
- Excellent at high temperatures.
Drawbacks
- Heavier and lower energy density (90-160 Wh/kg) for the same capacity.
- Larger volume may limit ultra-compact designs.
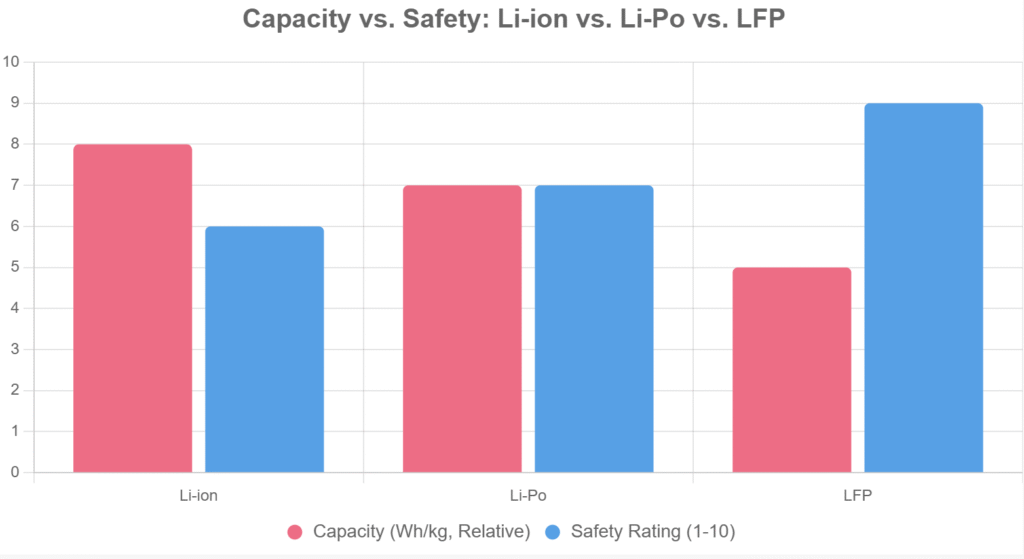
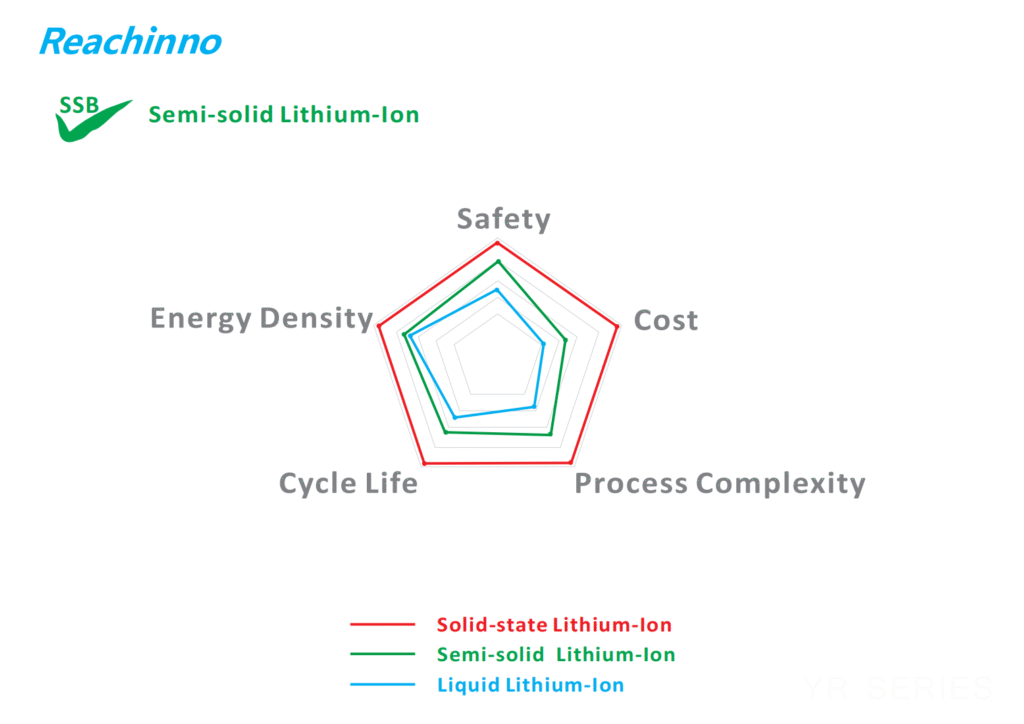
4. Semi-Solid Lithium Batteries
Overview
Emerging semi-solid-state batteries replace part of the liquid electrolyte with a polymer gel, providing better safety and energy density than Li-ion. In 2025, they’ve seen commercialization in China (e.g., CATL, NIO), with products like hybrid-solid state power banks offering gel-like electrolytes for higher density. They retain 5-10% liquid for easier production.
Advantages
- Higher thermal stability than Li-ion; safer for fast-charging.
- Energy density: 250-300 Wh/kg; cycle life: 1,000-1,500+.
- Enhanced performance and lifespan; ideal for high-power applications.
Drawbacks
- Still in limited mass production; costs 1.5x higher than Li-ion.
- Transitional tech before full solid-state.
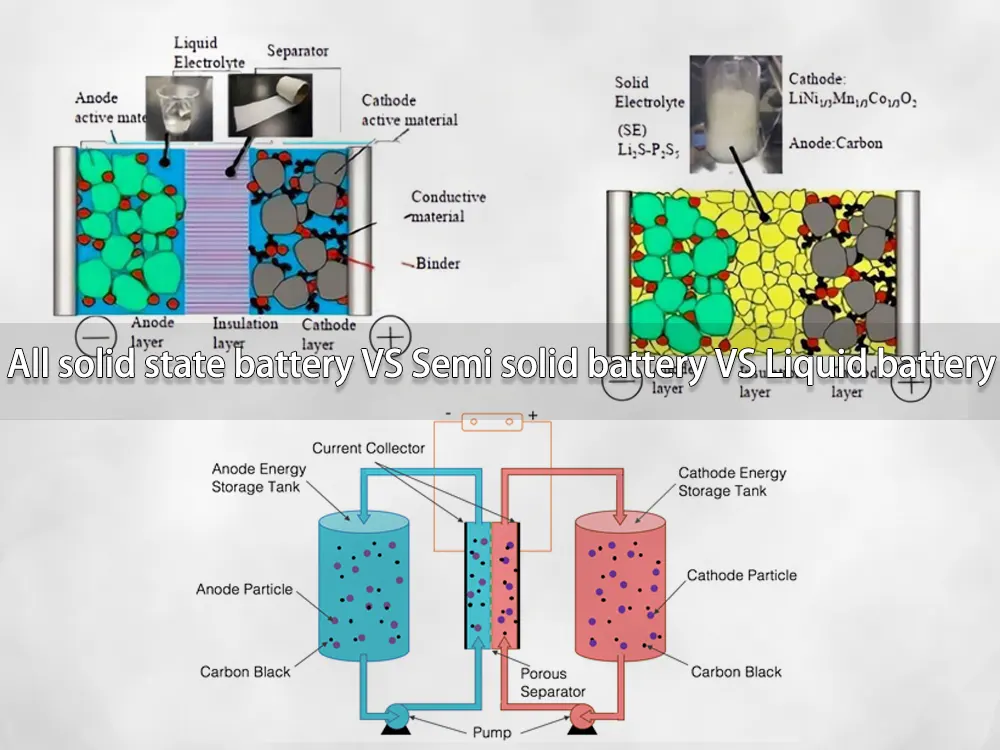
All solid state battery vs semi solid battery vs liquid battery …
5. Solid-State Batteries
Overview
Solid-state batteries completely eliminate liquid electrolytes, using solid (ceramic or polymer) layers for maximum safety. By 2025-2026, commercialization is advancing, with products like KU XIU’s 5000mAh magnetic charger and projections for 300-500 Wh/kg by companies like Toyota and Samsung.
Advantages
- Extremely low fire risk; improved safety and simplified designs.
- High energy density (350-500 Wh/kg); longer shelf life and cycles (3,000+).
- Potential for ultra-compact power banks.
Drawbacks
- Very high cost; manufacturing in R&D/pilot scale.
- Challenges like dendrite formation; limited OEM supply.
A) Schematic illustration of the all‐solid‐state lithium battery …
6. Key Considerations for OEM/ODM Sourcing
When selecting battery types for power banks, consider:
7. Safety & Thermal Management
Battery overheating is the leading cause of failures in power banks, stemming from high current discharge, hot environments, aging, defects, or overcharging. Modern batteries integrate:
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Monitors voltage, current, temperature, and includes cell balancing.
- Active Balancing ICs: Equalize cell charge to extend life and improve safety.
- Protections: Against overcharge, over-discharge, short-circuit, and thermal runaway.
Safe ranges: Operate 0-45°C; charge 5-35°C; store -20-25°C. Prevention: Use approved chargers, ensure ventilation, inspect regularly, avoid extremes.

How Much Do You Know About Battery Management System Block Diagram …
8. Trends in 2025 and Beyond
- Increased adoption of LFP and semi-solid for safer high-capacity power banks, with semi-solid already in products like Energea’s hybrid-solid state.
- Fast-charging protocols (PD 3.1, QC5.0) pushing chemistry limits.
- Wireless and magnetic charging support.
- Solid-state commercialization by 2026-2027 for premium devices, with energy densities up to 500 Wh/kg.
🏭 9. Why Choose Reachinno as Your Battery Partner
At Reachinno Innovation, we don’t just assemble power banks — we engineer them from the cell chemistry upward. 🌱 Our Advantages:
- 🧪 20+ years of manufacturing experience in consumer power electronics
- 🔋 Own R&D and testing center for cell matching, BMS optimization, and certification compliance
- 🧰 ODM/Customized project service — from concept to mass production
- 🛡️ Full certification coverage: UL, UN38.3, CE, RoHS, FCC, and CCC for semi-solid power banks (June 2025)
- 🌍 Trusted by global brands across Japan, the U.S., and Europe
With our LFP and semi-solid product line, we help brands achieve better safety, longer lifespan, and stronger market competitiveness — all while staying compliant with 2025’s latest safety regulations.
📊 10. Summary: The Future Is Semi-Solid
From the early Li-ion days to today’s semi-solid innovation, battery evolution has always been about one goal: safer, longer-lasting, smarter energy.
As the global market demands higher performance with tighter certification standards, Reachinno stands at the frontier, bringing semi-solid CCC-certified power banks to mass production — a true milestone in portable energy technology.
Ready to power the future? Contact Reachinno today for OEM/ODM solutions that meet 2025’s toughest standards. Contact Us | Explore Products
Last Updated: November 12, 2025 Keywords: power bank battery types 2025, Li-ion vs Li-Po vs LFP, semi-solid battery power bank, OEM power bank manufacturer, solid-state power bank technology

